
The eggplant (Solanum melongena L., 2n = 2x = 24), also known as brinjal eggplant or aubergine, belongs to the Solanaceae family. The bulk of eggplant production is concentrated in China, India, Iran, Egypt and Turkey, with Italy and Spain representing the most important European Union producers. After potato and tomato, it represents the third most important solanaceous crop species. Eggplant berries are a source of dietary minerals as well as vitamins and other health-promoting metabolites such as anthocyanins and chlorogenic acid, with nutraceutical and anti-oxidant properties.

Unlike tomato, potato and pepper, eggplant is native to the Old World and was independently domesticated from Solanum insanum L. in the Indian subcontinent and in China, with a possible additional and independent center of domestication in the Philippines. Besides S. melongena, two other eggplant species are commonly grown in sub-Saharan Africa, the scarlet eggplant (S. aethiopicum L.) and the gboma eggplant (S. macrocarpon L). Both species can be inter-crossed with brinjal eggplant producing hybrids with intermediate fertility.
Eggplant diversity
A wide collection of eggplant breeding lines, heritage varieties and selections within local landraces provenanced from Asia and the Mediterranean Basin was recently phenotyped with respect to key plant and fruit traits, and genotyped using microsatellite and SNP loci distributed uniformly throughout the genome (Cericola et al. 2013 PLoS ONE 8:e73702; Cericola et al. 2014 BMC Genomics 15:896; Portis et al. 2015 PLoS ONE 10:e0135200). The panel formed two major clusters, which to a large extent mirrored the provenance of the entries.
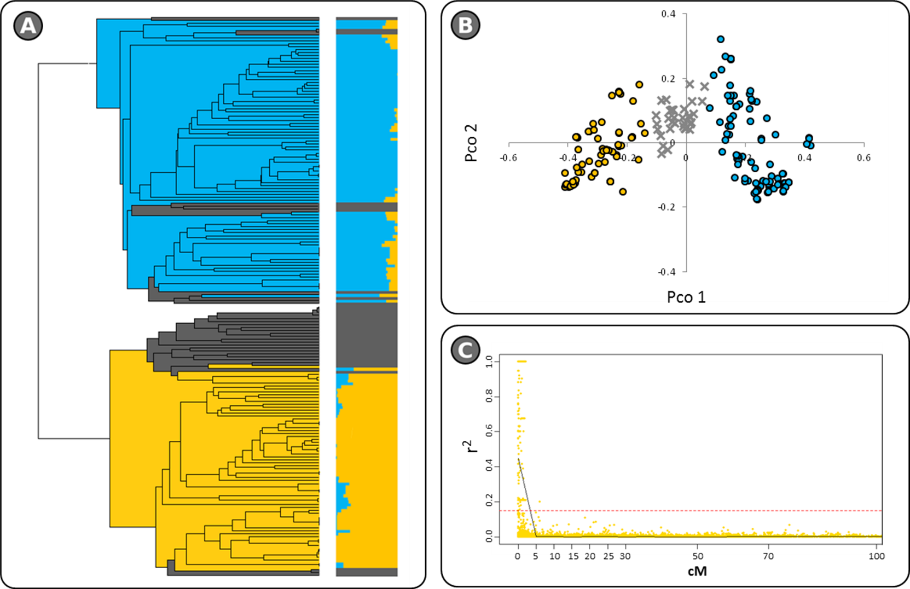
The genetic architecture of the full germplasm panel. A) UPGMA dendrogram derived after taking account of the STRUCTURE analysis. B) PCoA visualization of the genetic relationships C) Linkage disequilibrium decay (From Cericola et al. 2014 BMC Genomics 15:896).
191 Members of the germplasm panel were deliberately selected to represent the full range of phenotypic diversity in eggplant and scored for a set of 19 fruit and plant traits in a replicated experimental field trial. The phenotypic data were subjected to principal component and hierarchical principal component analyses, allowing three major morphological groups to be identified.
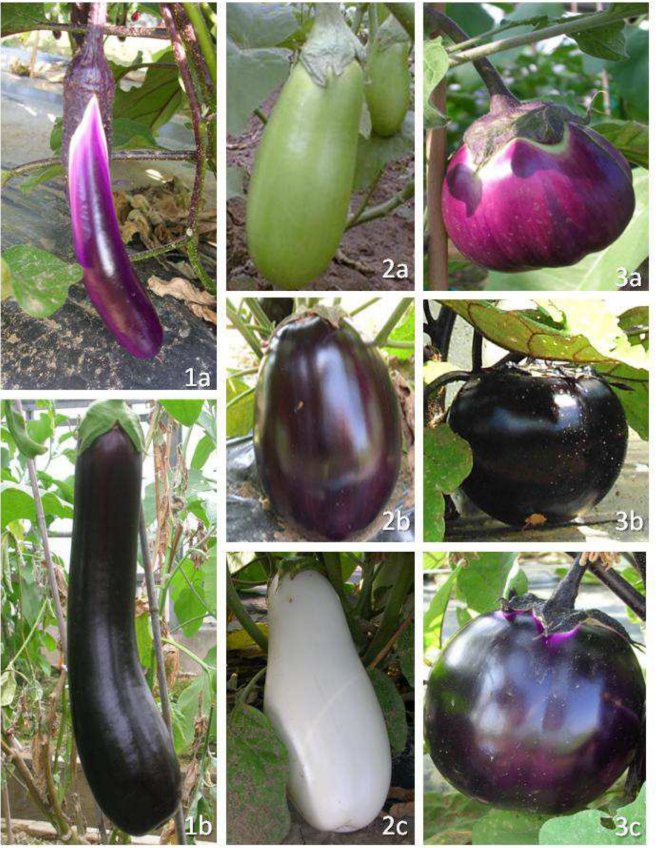

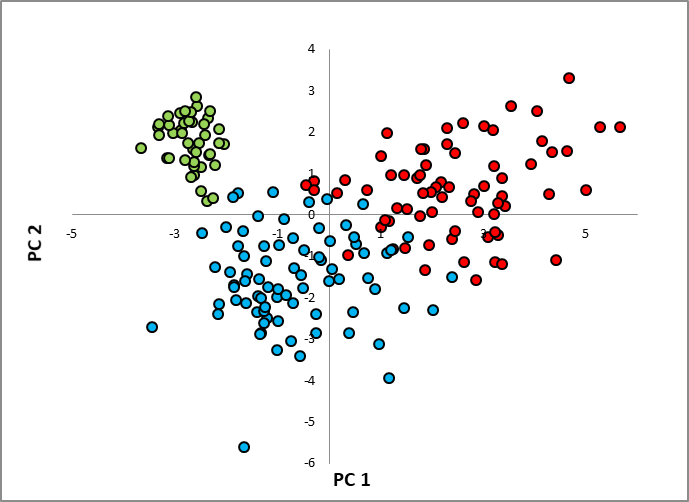
Principal coordinates analysis based on the leading two PC’s and fruits of accessions belonging to the three main morphological groups Entries belonging to each morphological group marked by a different color (red: group 1, blue: group 2,green: group 3) (From Cericola et al. 2013 PLoS ONE 8:e73702).
